Just before the monthly Washington Aero Club luncheon—hosted by the National Business Aviation Association (NBAA)—kicked off on Thursday, I was chatting with two members of of the general media whom I had not yet met. One represented Bloomberg’s tax-related publications and was relatively new to the beat. The other reported for the Wall Street Journal’s general business coverage, and had not delved much into private aviation (aside from a stint sitting next to Jon Ostrower while he was still at the WSJ, from whom he said he soaked up aerospace insight like a sponge).
The pair each echoed in their own words the fact they had been invited to a panel on sustainability in business aviation—yet before that moment, had no idea that those flying BA had any desire to act sustainably. “I had no idea anyone flying private jets cared,” was the consensus.
I know in theory how true it is that we often preach to our own choir in BA/GA, but once more I was slapped in the face with proof.
First, kudos to NBAA for bringing these two reporters from the general media (among others) into a room where they would hear an up-to-date and frank accounting from three leaders in our space that sit at the tip of the sustainability spear: Michael Amalfitano, president and CEO of Embraer Executive Jets, Billy Nolen, former deputy FAA Administrator and chief regulatory affairs officer for Archer Aviation, and Scott Lewis, president of World Energy (WE) SupplyZero, one of the largest producers of sustainable aviation fuel in the United States and globally.
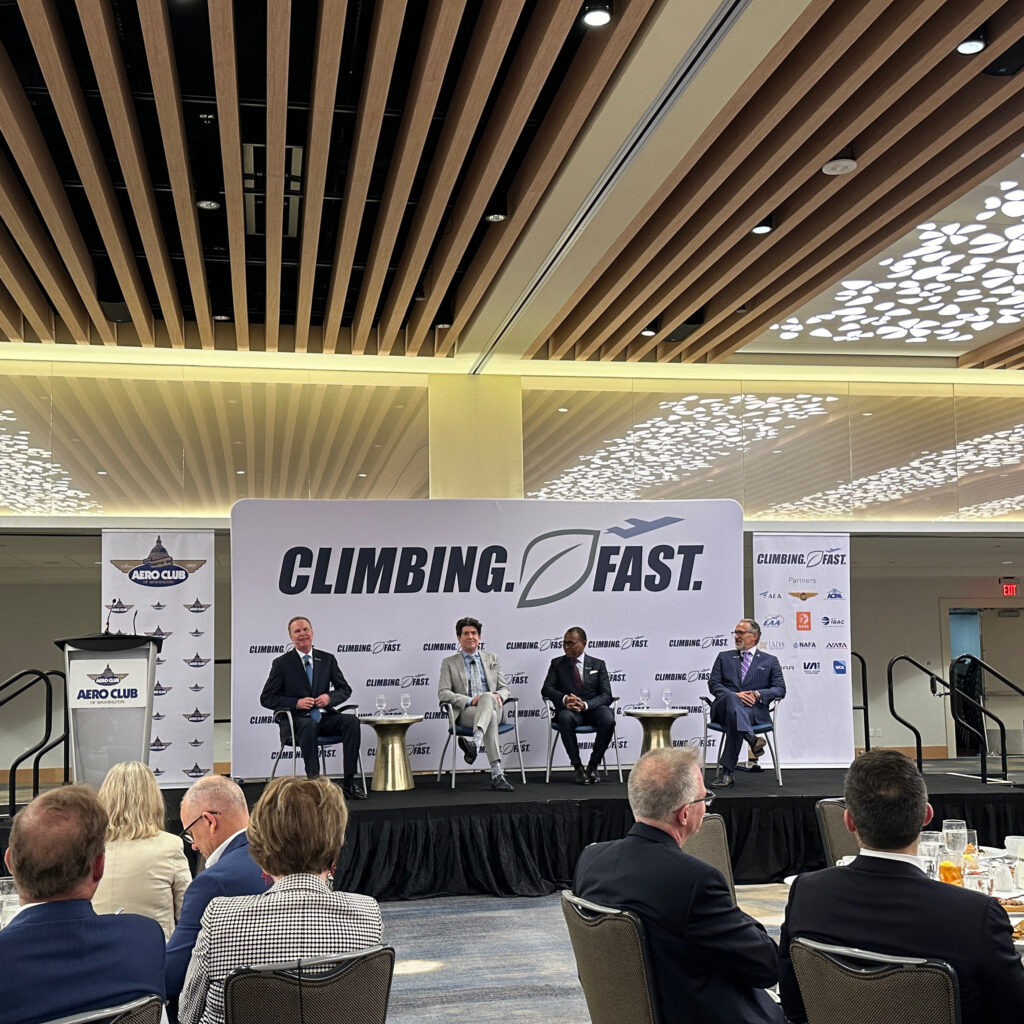

In summary, here’s where we are in terms of the three pillars remarked upon by Amalfitano, Nolen, and Lewis—and underlined by moderator Ed Bolen of NBAA:
Commitment from the Manufacturers: Embraer now uptakes weekly the volume of SAF it had delivered quarterly in 2023. Amalfitano noted the Brazilian OEM had tested to 100 percent—”neat”—SAF in its Phenom 300 and Praetor 600, and that it uses the fuel in various blends for test flight, demos, and customer deliveries. “That will allow us to increase what was a low mid-single-digit consumption of SAF to 20 to 25 percent of what we do out of Melbourne” in 2024, he said. Embraer has cooperated with its engine OEM partners, including Honeywell, through the process.
Legislative Synergy for Sourcing and Distribution: Lewis outlined how WE SupplyZero is growing volume at the best rate possible, producing SAF derived from animal fats and used cooking oil. “We are employing latest technology that’s available right now in order to take that up from where we are today,” said Lewis. “About 4,000 barrels a day, of which about 1,000 barrels is sustainable aviation fuel, up to 25,000 barrels a day, of which 20,000 barrels is sustainable aviation fuel.” WE is also working on a pipeline that will deliver from its main terminal in the Los Angeles area (and soon to come in Houston), in order to reduce the overall carbon footprint of the SAF, so that its benefit is not just zero emissions from aircraft exhaust, but through the entire chain. Leaders in the audience noted the passing of the most recent agriculture funding bill in synergy with the last infrastructure funding bills and FAA Reauthorization Act to support biodiesel production in the U.S. The Biden Administration has challenged the industry to produce 3 billion gallons per year of SAF by 2030.
Advanced Air Mobility Goes Electric: Along with Amalfitano, who outlined Embraer’s electric push with its stake in Eve (an electric VTOL), Nolen reported on Archer’s leadership in bringing a viable eVTOL to market, with the regulatory basis established, airline partnerships in play, and a roadmap to infrastructure to support the accelerated development. He brought up another key feature of moving eventually to electric power: the quiet needed to fly within residential communities. “How have we gotten to this point?” said Nolen. “Three critical things have happened. Number one, battery cell technology has gotten us to the point that we have…the carrying capacity. Number two, the FAA has given us a regulatory path to get there. And number three, we’ve had the level of federal investment which, in turn, has unlocked the financial investment.”
All three areas will be required to maintain at least the current pace—and accelerate—in order to continue what BA has managed to accomplish in increased efficiency over the course of the last 40 years. Because the 30 percent greater efficiency gains that we have seen with each new bizjet model over that timeframe aren’t going to be enough to cover the spread in the future.